WAJ Projects Achieved (2024-2026)
The WAJ Database of Animal Laws is expanding to other regions of the world! After Asia, Africa was the next priority region identified to share existing laws and provisions to protect animals, empowering animal advocates, and fostering animal law enforcement and reforms in Africa.
AFRICA
Discover WAJ African Database of Animal Laws
Led by World Animal Justice (WAJ) in collaboration with the Lawyers for Animal Protection in Africa (LAPA), this database compiles and presents the laws protecting animals -with emphasis on animal anti-cruelty laws- present in African countries, covering +130 animal laws in 51 countries, as well as those adopted by regional organisations and the African Union -which adopted the Animal Welfare Strategy for Africa and the 2024 Ban on Donkey Skin Trade.
Worldview of Animal Anti-Cruelty Laws
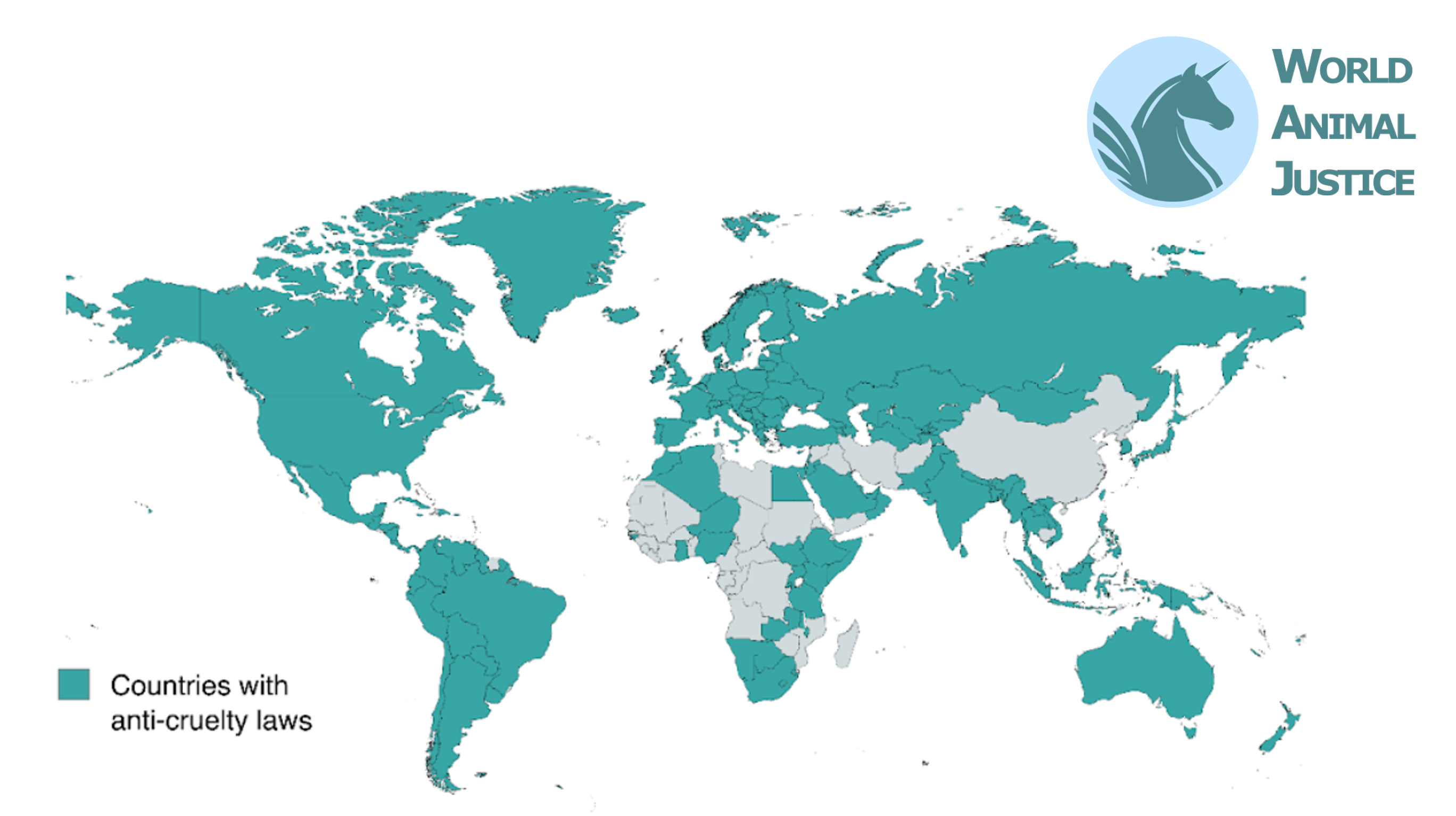
4/5 of world’s countries have at least basic anti-cruelty laws (in green) where 1/5 still don’t (in grey)
→ 4/5 of the world’s countries have at least some form of basic anti-cruelty laws (in green) whereas 1/5 still don’t (in grey)
Many of the green countries also have general animal protection laws, specific activities and practices involving animal abuse, with around 10 countries worldwide having constitutional provisions to protect animals. Pioneer countries in South America and the Indo-Pakistani region have adopted some of the first court decisions on animal rights.
However, there is still a long way to go to protect all animals from the massive crimes they are legally victims of every day worldwide for food, experiments, hunting etc. WAJ research led in 2024 on the legal protection of animals against criminal acts discovered a striking fact:
● Less than 5% of animals are protected by anti-cruelty laws (mainly companion animals) with enforcement issues.
● It is less than 1% when including other sentient aquatic and invertebrates (eg: fish, cephalopods, decapods ect). In this sense, while many animal health and welfare laws exist to regulate the use of animals in farming, transports, slaughters or experiments, they aim more at reducing the worst pain suffered by animals, rather than allowing a real well-being for these animals who are still legally tortured (e.g. live mutilations), sequestrated (e.g. small cages) and massively murdered on a daily basis, with at least 500 million terrestrial animals killed every day for food alone.
Add Your Heading Text Here
Regional overviews of animal law obligations and prohibitions
EUROPE
Constitutional & Anti-Cruelty Animal Laws Overview
In 2024, we gathered the last available laws in the European countries to underline the following information:
– A brief comparison of anti-cruelty laws in the 27 EU countries to underline the common points & top punishers;
– A brief overview of the evolution of Constitutional provisions for animals in European countries in June 2024.
Anti-Cruelty Laws in EU Countries
To date, every EU country has anti-cruelty laws. ‘Cruelty’ is usually defined as inflicting ‘unnecessary’ suffering (knowing that these laws tend to be restricted to companion and/or vertebrate animals). Zoophilia is prohibited.
Aggravated cruelty is usually committed when involving the death of the animal, many animals, recidivism etc.
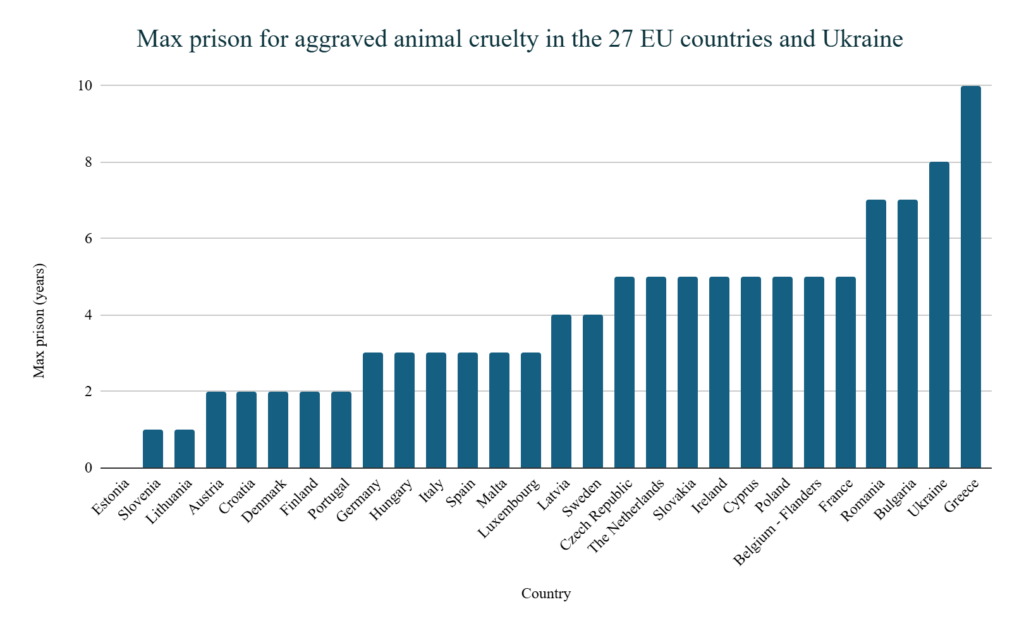
Who are the top punishers (in theory)? Which countries impose the highest penalties under their criminal laws?
-> Prison: Bulgaria and Romania provide up to 7 years, and Greece provides the most with up to 10 years in prison!
-> Fines: Spain and Luxembourg provide with up to 200,000 euros and Ireland with up to 250,000 euros!
In practice, we can observe a general lack of enforcement, knowing that the penalties decided by the Judges are usually lower than the maximum provided. However, a recent trend indicates that the penalties provided for animal cruelty are constantly increasing. In 2023 and 2024, four EU countries increased maximum prison sentences by 1-3 years: Croatia, Slovakia, Portugal, and the Netherlands.
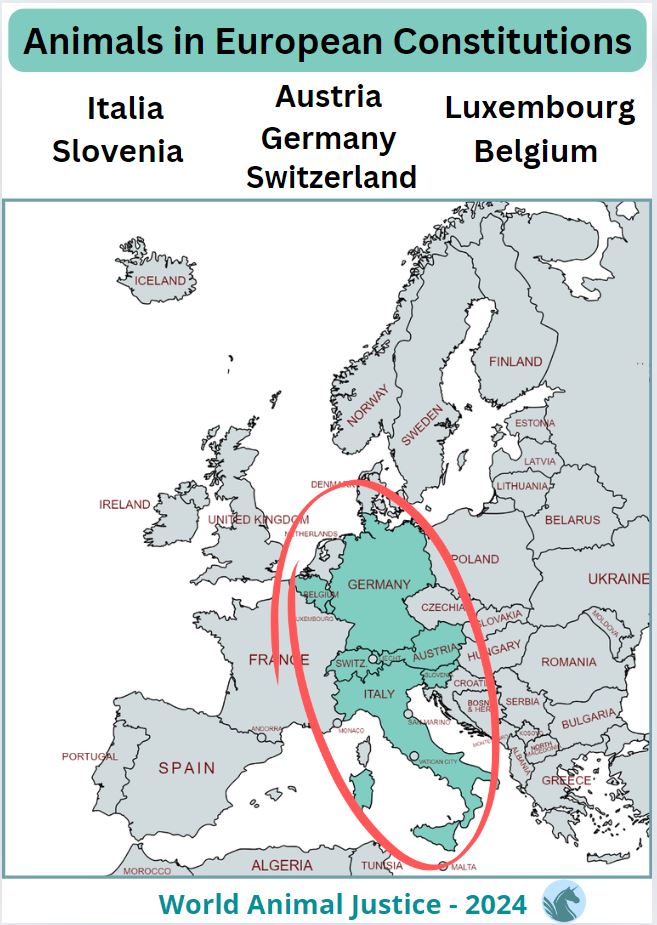
Animals in European Constitutions
At the highest level of the laws, the role of Constitutions is to ensure the rights and duties of the citizens in every country.
– Slovenia: Since 1991, Constitution (Art. 72) states that “the protection of animals from cruelty” shall be regulated by law”.
– Switzerland: Since 1992, the Swiss Constitution (art.120) provides for the “dignity of living beings” in biotechnology.
– Germany: Since 2002, the German Constitution (art.20 A) explicitly includes the “protection of animals”.
– Luxembourg: Since 2007, the Constitution (art.11 bis) provides for the “protection and welfare of animals“.
– Austria: In 2013 the Federal Constitutional Law on “sustainability and animal welfare“.
– Italia: Since 2022, the Italian Constitution (art.9 al.3) provides the need to “safeguard animals“.
– Belgium: Since May 2024, the Constitution (art.7 bis) includes “the protection and welfare of animals as sentient beings”.
Interestingly, we can observe that this progression concerns neighboring countries in the same region of Central Europe.
If you want to share other updates, please contact us via the Contact form Join us
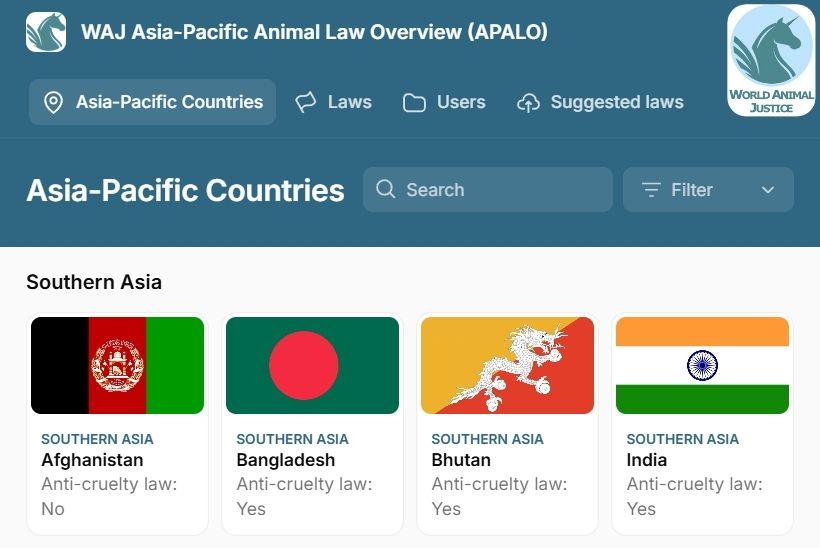
ASIA-PACIFIC
Asia-Pacific Animal Law Overview (APALO)
Laws are importan instruments to better protect animals. However, these laws can be hard to access in some regions of the world. To clarify what actions are prohibited against which animals in Asian countries and to empower global animal advocacy, World Animal Justice (WAJ), in partnership with the Institute of Animal Law of Asia (IALA) and with the support of the Asia for Animals (AfA) Coalition launched the Asia-Pacific Animal Law Overview (APALO).